Alloys made with a combination of titanium and other chemical components are known as titanium alloys. These alloys have great tensile strength (even at high temperatures). In addition, they are lightweight, have remarkable corrosion resistance, and can withstand extremely high temperatures. Nevertheless, the high cost of both the raw materials and the processing restricts their use to medical uses, airplanes, bikes, medical devices, jewelry, and highly stressed parts like the connecting rods on expensive sports cars, as well as some premium sporting goods and consumer electronics. Read More…
Banner Service Corp., serving the precision machining industry since 1961, is a premier provider of cold finished bar solutions, offering titanium & exotic alloys for a variety of applications, including medical grade titanium bar products. Extensive inventory and unmatched precision processing capacity & capabilities for ground bars & tubing, and even machined parts, with very short lead times.

Future Metals’ focus is providing aircraft-grade titanium and other metal products to the aerospace industry. We offer titanium tubing, titanium sheet and titanium bar. We also distribute tubing, stringers & extrusions, sheet and bars in aluminum, alloys, high-temperature metals and stainless steel.
All Titanium Metals is a leader in the titanium industry, embodying a commitment to excellence as your trusted titanium supplier. In our unwavering pursuit of providing top-notch commercially pure-grade titanium products, we take immense pride in our high quality products.

Online Metal Supply is your surplus metal warehouse offering guaranteed low prices for round titanium rods in different diameters & lengths and titanium sheet & plate in various dimensions. Plus, aluminum, brass, bronze, copper, magnesium, laminates, plastics, specialty alloys, steel and stainless steel too.
As an international producer of medical-grade products using our leading precision medical titanium wire, Fort Wayne Metals is a leader in medical wire. Since 1946, we have offered titanium and titanium alloys, round wire, flat wire and cables. Our medical wire ranges in diameter from .0005 - .250 inches.

More Titanium Alloy Suppliers

Alloy Production
Titanium alloys must first be created before being used to create parts and other items. To do this, manufacturers most frequently start with a melted or powdered form of titanium and then carefully measure out other metal powders or liquids. Next, they combine the ingredients to create the desired combination, melt it, and then press it into a die. To manufacture stock items like slabs, bars, rods, foils, profiles, strips, tubes, shims, sheets, plates, and wire, the mold, in these instances, is always in the shape of a stock shape.
These stock shapes make it simple to manage warehouses, dispatch products to manufacturers, and transport finished goods. Alloy production produces a variety of products. For instance, aluminum-titanium alloys are more durable and refined than either aluminum or titanium used separately.
Additionally, titanium metal is lighter and more corrosion-resistant compared to normal steel. Because manufacturers can utilize various forming techniques to build their goods, they can also meet a wide range of industry and consumer needs. They use various techniques to create titanium alloy products, such as cold forming, castings, forging, flat rolling, extrusion, hot forming, machining, welding, and spinning.
Types of Titanium Alloys
- Alpha Alloys: Commercially pure titanium is alloyed with trace amounts of oxygen to increase its tensile strength and hardness. By varying the amounts applied, it is possible to produce a variety of commercially pure titanium classes with strengths ranging between 290 to 740 MPa. These substances are theoretically entirely alpha in structure, yet minute quantities of beta phase are feasible if the beta stabilizers' impurity levels, such as those of iron, are sufficient. While adding around 2.5 percent of copper to titanium results in a product that reacts to solution processing and aging similarly to aluminum-copper alloys, alpha alloys cannot be heat treated to boost strength. When titanium is alloyed with other commercially available alloys, aluminum acts as an alpha stabilizer.

- Alpha-Beta Alloys: Iron, molybdenum, vanadium, and chromium stabilize the beta phase, and several other alpha-beta alloying elements have been developed. These materials typically range from medium to high strength, with tensile strengths between 620 and 1250 MPa and creep tolerance between 350 and 400°C. Fracture toughness and low- and high-cycle fatigue are becoming more crucial design factors. To ensure that the alloys offer the greatest mechanical qualities for various applications, heat treatment and thermomechanical techniques have been devised. Alloys close to alpha are used for the greatest creep tolerance at temperatures exceeding 450°C. In addition, they offer adequate creep strength at temperatures of up to 600°C.
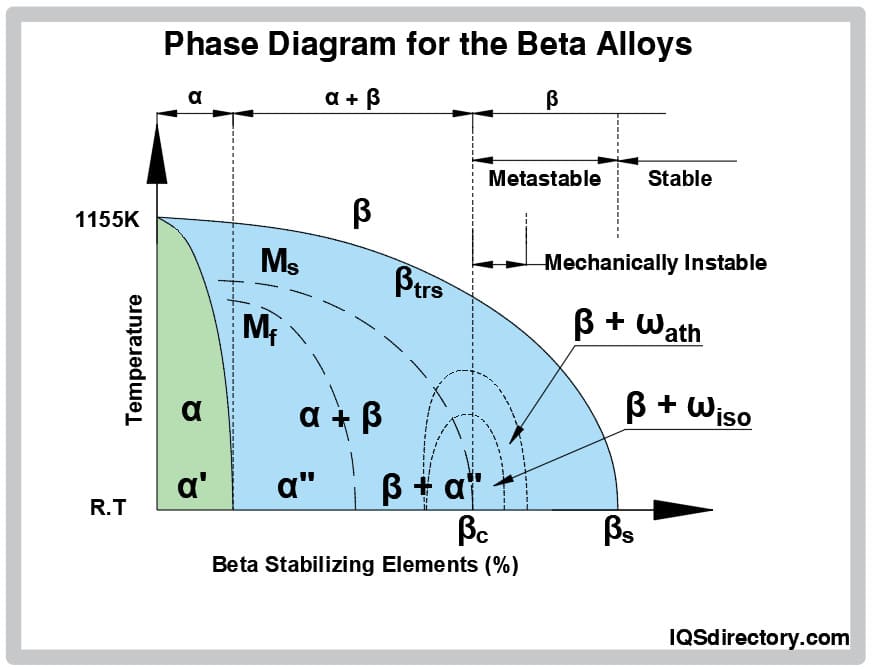
- Beta Alloys: The other class of titanium material is known as a beta alloy. All-beta alloys can be produced if a good quantity of beta-stabilizing components is added to titanium. Although these substances have existed for a while, their appeal has recently increased. They can be heat processed to high strengths, are easier to work hard than alpha-beta alloys, and have better resistance to corrosion than economically pure grades. There are specifications for titanium materials used in aircraft; however, none exist for metals used in non-aerospace applications.
Applications of Titanium Alloys
An alloy is made by gently altering the characteristics of each component to keep and improve each one's best attributes. Because they are simpler to work with than pure titanium, which is quite hard despite not being dense, titanium alloys are quite popular. Titanium is typically alloyed with iron and aluminum, tin and vanadium, manganese, or molybdenum to facilitate processing and manufacture. Although titanium already has many beneficial qualities, these substances can improve titanium’s inherent strength, heat resistance, and corrosion resistance.
Exhaust systems, rocket engines, motorcycles, missiles, spaceships, paint, plastics, and valve springs are examples of the numerous goods that utilize titanium alloys. As a result, aerospace, aquariums, automotive, desalination, electronics, jewelry manufacture, army and defense, power generation, and shipping are just a few of the numerous industries that use titanium alloy goods.
Choosing the Correct Titanium Alloy Company
To make sure you have the most productive outcome when purchasing titanium alloys from a titanium alloy company, it is important to compare at least 4 to 5 companies using our titanium alloy directory. Each titanium alloy company has a business profile page that highlights their areas of experience and capabilities and a contact form to directly communicate with the company for more information or request a quote. Review each titanium alloy company website using our proprietary website previewer to get an idea of what each company specializes in, and then use our simple RFQ form to contact multiple titanium alloy companies with the same quote.







 Alloy Suppliers
Alloy Suppliers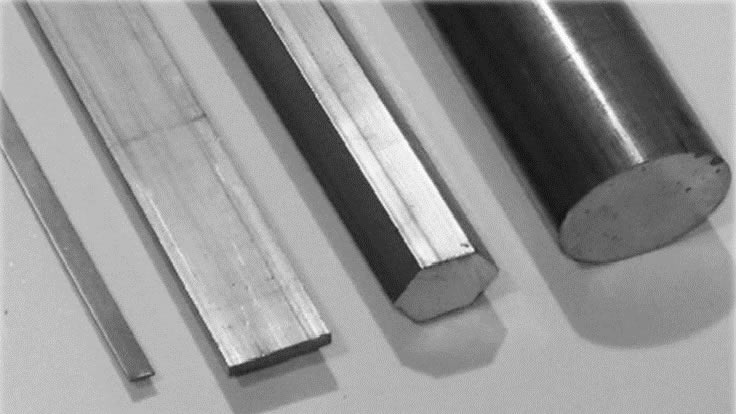 Aluminum
Aluminum Aluminum Extrusions
Aluminum Extrusions Copper-Brass-Bronze
Copper-Brass-Bronze Magnets
Magnets Nickel
Nickel Stainless Steel
Stainless Steel Stainless Steel Tubing
Stainless Steel Tubing Steel Service Centers
Steel Service Centers Titanium
Titanium Tungsten
Tungsten Wire Rope
Wire Rope Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services